UART串口通讯原理
UART串口通讯原理
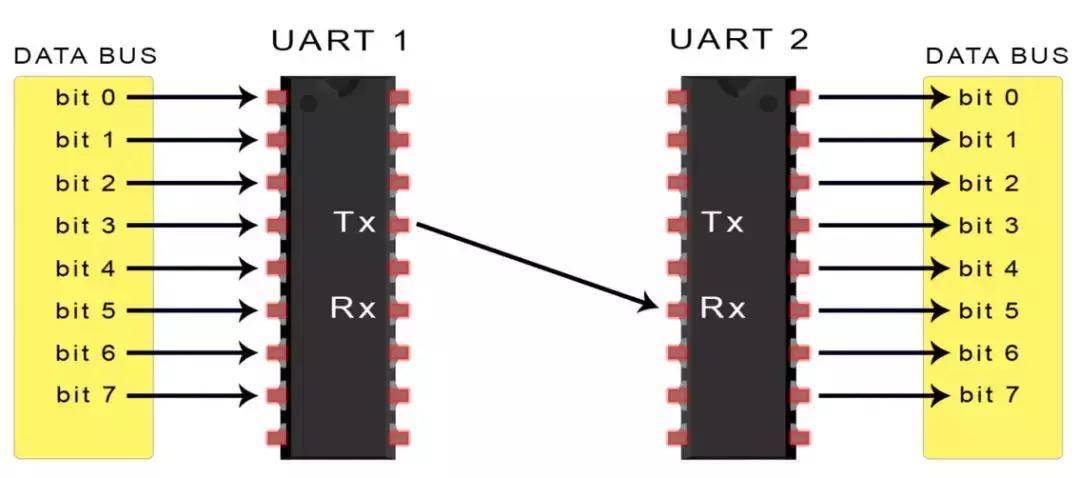
通用异步收发传输器(Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter),通常称作UART。它将要传输的资料在串行通信与并行通信之间加以转换。作为把并行输入信号转成串行输出信号的芯片,UART通常被集成于其他通讯接口的连结上。
特点
- 只需要定义两个针脚
- 异步通讯
如何工作
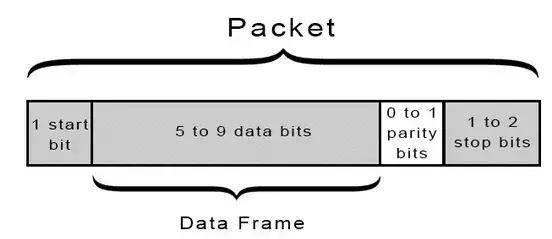
UART传输数据依靠的是UART总线,数据总线用于通过CPU,存储器或微控制器等其他设备将数据发送到UART。数据以并行形式从数据总线传输到发送UART。在发送UART从数据总线获得并行数据之后,它将添加起始位,奇偶校验位和停止位,从而创建数据包。接下来,数据包在Tx引脚上逐位串行输出。UART接收端则在其Rx引脚上逐位读取数据包。然后,接收UART将数据转换回并行形式,并删除起始位,奇偶校验位和停止位。最后,接收UART将数据包并行传输到接收端的数据总线。
- 并行转换为串行
- 添加起始位 奇偶效验位 停止位,打包
- Tx引脚逐位输出
- Rx接收端读取数据包
- 解包
MicroPython-UART
文档参考:https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/library/pyb.UART.html#pyb-uart
例子
创建和初始化UART对象
1 | from pyb import UART |
初始化分别设置传输位,校验位,停止位
UART读写操作
1 | uart.read(10) # read 10 characters, returns a bytes object |
方法
1 | UART.init(baudrate, bits=8, parity=None, stop=1, *, timeout=0, flow=0, timeout_char=0, read_buf_len=64)¶ |
- Baudrate 波特率
- bits 数据比特位数
- parity 效验位
- stop 停止位
- flow 流控制
- Timeout
1 | UART.deinit() |
关闭UART总线
1 | UART.any() |
返回等待读取的比特流
1 | UART.read([nbytes]) |
读取字符。nbytes设置每次读取最大字节数
若不设置nbytes,则返回最多字符
Note: for 9 bit characters each character takes two bytes,
nbytesmust be even, and the number of characters isnbytes/2
返回值:读取的比特流对象,超时返回None
1 | UART.readchar() |
接受单个字符
返回值:返回一个字符,超时返回-1
1 | UART.readinto(buf[, nbytes]) |
从缓冲区读取比特流。nbytes指定读取最大比特
返回值:返回读取在buffer中的比特数。
1 | UART.write(buf) |
Write the buffer of bytes to the bus. If characters are 7 or 8 bits wide then each byte is one character. If characters are 9 bits wide then two bytes are used for each character (little endian), and
bufmust contain an even number of bytes.Return value: number of bytes written. If a timeout occurs and no bytes were written returns
None.
1 | UART.writechar(char) |
Write a single character on the bus.
charis an integer to write. Return value:None. See note below if CTS flow control is used.
解包数据
1 | if uart_A.any(): |
